What is Chemobrain and how it affects cognitive function
Although the physical symptoms of chemotherapy are widely known (such as fatigue, dizziness, weight loss, alopecia) there are also patients who experience cognitive symptoms. This is known as chemobrain.
What is chemobrain or chemofog?
Chemobrain consists of a series of cognitive symptoms and impairments caused by chemotherapy treatment, not necessarily linked to the patient’s type of cancer. The toxicity, inflammation, immune response or oxidative stress generated by chemotherapy could be factors that influence cognitive functioning.
These cognitive symptoms negatively affect the patient’s quality of life in both the short and long term.
What are the main cognitive impairments due to chemotherapy?
The main cognitive functions impaired due to chemotherapy are:
- Attention:
- Impaired alternating attention: difficulty performing more than one task at a time or multitasking.
- Mental fog and difficulty focusing on one thing for a continuous period of time.
- Memory:
- Impaired short-term memory: trouble remembering dates, names or events.
- Language:
- Impaired lexical access and word finding difficulties (anomia).
- Executive functions:
- Slow processing speed.
- Difficulty in planning and problem solving.
How long do the effects of chemotherapy on cognition last?
The effects of chemotherapy on cognition can vary in duration:
- During chemotherapy: During chemotherapy treatment, Chemobrain symptoms may be more pronounced due to the high concentration of the treatment and toxicity on the body. Patients may experience cognitive difficulties such as memory loss, difficulty concentrating, problems with information processing and changes in processing speed. .
- After completing chemotherapy: After completing chemotherapy treatment, some people experience gradual improvement in their symptoms. However, for others, symptoms may persist or even temporarily worsen before improving. This can last for weeks or months.
- Long-term: For some people, Chemobrain symptoms may persist long-term, even after months or years have passed since the end of chemotherapy.
How and when to treat Chemobrain.
To improve cognitive functions affected by chemotherapy, various treatments can be effective:
- Cognitive stimulation and cognitive exercises.
- Physical exercise.
- Occupational therapy.
- Cognitive compensation techniques.
- Stress management and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
- Healthy diet.
- Rest.
These types of interventions can be beneficial both during and after chemotherapy. They may also be effective in treating the long-term effects of Chemobrain.
Rehametrics exercises to improve the effects of Chemobrain
Rehametrics offers both cognitive and physical exercises. It allows to personalize activities to the specific needs of each patient, adjusting the difficulty depending on patient performance. The activities are motivating for the patient and the software provides direct feedback on their performance. In addition, Rehametrics provides results and reports that allow healthcare professionals to continuously adjust the treatment.
Rehametrics cognitive software offers more than 160 activities specialized in treating various cognitive symptoms caused by the side effects of chemotherapy.
Exercises to rehabilitate different types of attention:

Divided attention exercise: The patient must select stimuli with the same shape or form depending on which side they are presented.
Exercises to rehabilitate and train memory:
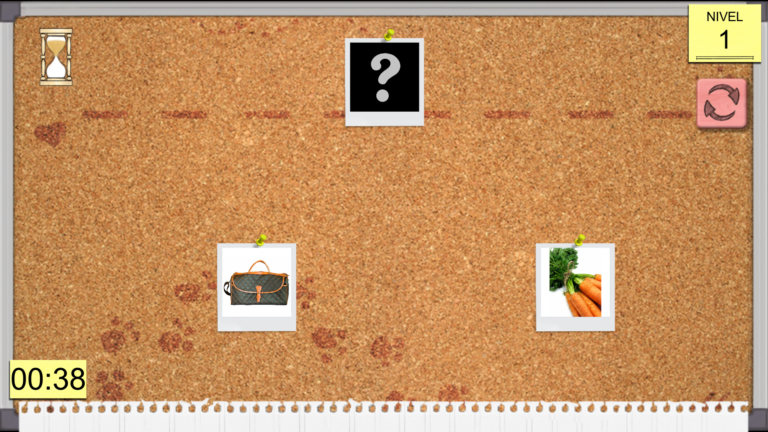
Delayed memory exercise: The patient must remember a series of images, after completing an interference task.
Exercises to rehabilitate and train lexical access and language:
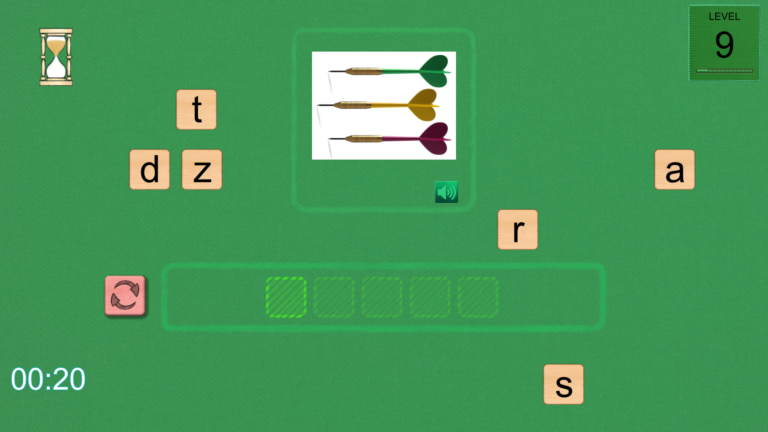
Naming exercise: The patient must select letters, in the correct order, corresponding to an image.
Exercises to rehabilitate and train planning and problem solving:

Instrumental Activities of Daily Living: The patient must decide the necessary steps to travel from one stop to another in a public transport system.
Likewise, by using the physiotherapy exercises offered by Rehametrics, physical exercise can be used by cancer patients in order to improve Chemobrain.
Using this type of activities from the onset of first symptoms of cognitive impairment after chemotherapy can improve the quality of life and cognitive function of cancer patients.
If you are a rehabilitation professional working with cancer patients in physical or cognitive therapy, we invite you to discover how our platforms can help with the cognitive side effects of chemotherapy.


